Content
Published:
This is an archived release.
Adult learning associations arranged 42 400 courses
Adult learning associations arranged 42 000 courses with 478 000 participants and 1 348 000 lessons in 2012. In spite of fewer courses, the number of participants increased compared to the previous year.
| 2012 | |
|---|---|
| Courses | 42 356 |
| Participants | 477 719 |
| Males | 205 102 |
| Females | 272 617 |
| Lessons total | 1 348 494 |
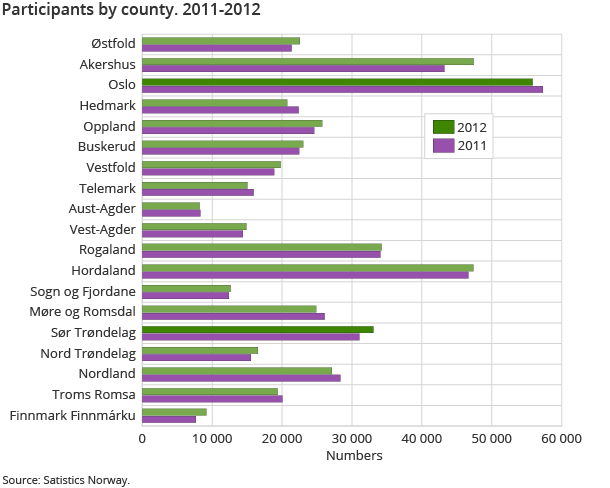
There were 7 000 more participants in 2012 compared with 2011. Akershus County had the highest increase, with 4 200 more participants. On the other hand, Hedmark County had the highest decrease, with 1 700 fewer participants.
Finnmark County had the highest percentage increase in number of participants, by 20 per cent, in 2012 compared with 2011.
Women in the majority
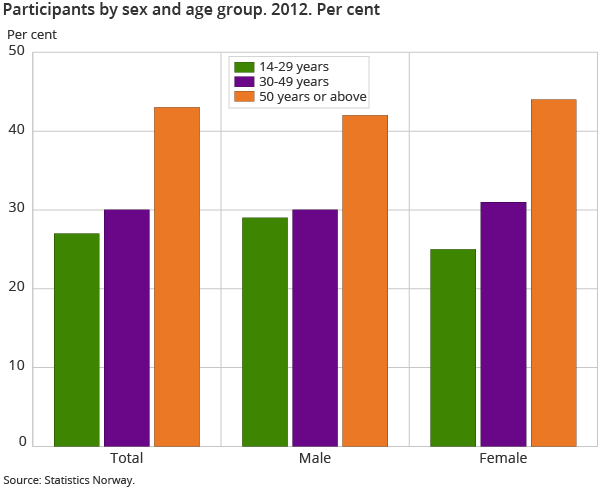
There were 7 700 more women and 700 fewer men in 2012 compared to the previous year. Women made up 57 per cent of all participants, while 43 per cent of all participants were men in 2012.
The number of participants in the age groups 14-29 and 50 and above increased for both women and men. The age group 14-29 had the highest increase in number of participants, with 4 400 more participants.
Participants chose aesthetic subjects and handicraft
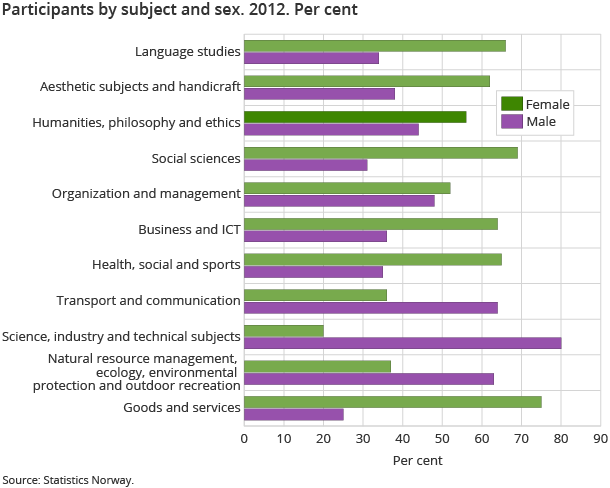
As in previous years, aesthetic and handicraft courses were the most popular courses. Adult learning associations arranged 17 700 courses with 219 100 participants within aesthetic subjects and handicraft in 2012. A total of 210 courses with 1 400 participants were arranged within goods and services subjects.
Female participants dominated in most main subjects. Courses with high female percentages were goods and services (75 per cent), social sciences (69 per cent) and languages (66 per cent). On the other hand, men accounted for 80 per cent of all participants within science, industry and technical subjects.
Contact
-
Hossein Moafi
E-mail: hossein.moafi@ssb.no
tel.: (+47) 90 40 31 19