Content
Published:
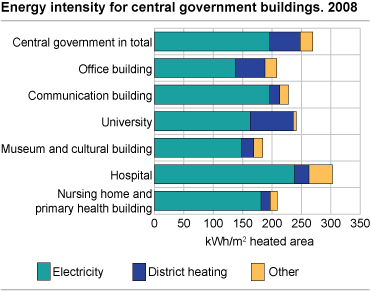
Highest energy use in hospital buildings
In 2008, average energy use in a sample of buildings within the Central government was 268 kWh/m2. Hospital buildings used 304 kWh/m2 and had the highest energy use per square metre, while the average energy use in Central government office buildings was 207 kWh/m2.
The total heated area in the buildings constituting this survey of energy use in the Central government is approximately 4.5 million square metres, and the majority of the buildings are of a relatively large size.
Period of energy use plays a crucial role
The very large energy use per square metre in hospital buildings can be explained by substantial energy intensive hospital equipment and long period of energy use. While there is normally activity both day and night in hospital buildings, average period of energy use in Central government office buildings is approximately 9 hours a day.
Large variations in energy use per square metrebetween and within different building types can also be explained by differences in building constructions, area of application, the amount of electrical equipment and the scope of implemented energy efficiency measures. Geographical location (temperature) is also an important element.
In 2008, the average specific energy use of heated areas in universities and colleges was 241 kWh/m2 . The reason why average energy use was lower in universities and colleges compared to hospital buildings can mainly be explained by longer periods of energy use in hospital buildings.
Energy use in office buildings among the lowest
The energy use in office buildings within Central government was 207 kWh/m2, and was among the buildings with the lowest specific energy use. Average time of energy use for all buildings in the sample was 17 hours a day.
Comparisons with figures from the statistics Energy use within the Service industries show that office buildings within the Central government had lower energy use per square metre heated area than other service industries. While the energy use in office buildings within the Central government in 2008 was 207 kWh/m2, the energy use in office buildings in other industries was 249 kWh/m2 in the same year. Other industries consists of private, municipal, county administrational and public enterprises not included in StatRes.
Comparisons of energy use in buildings between the Central government and other industries also show a variation in the use of energy sources. Electricity is the largest used energy source in most building types, but for buildings within the Central government district heating accounts for a higher share and use of electricity a lower share than what is seen in other industries.
Electricity is the largest energy source
Electricity is the largest used energy source and made up 73 per cent of total energy use in buildings within the Central government. District heating was the second largest energy source, with 19 per cent of total energy use, while heating oil accounted for 4 per cent of total energy use.
Among those building types that use a high share of district heating are universities and colleges. The share of district heating accounted for 30 per cent of total energy use in these buildings. In office buildings, the share of district heating accounted for 24 per cent. In hospital buildings, the use of electricity was a more dominant source of energy than for other types of buildings. In hospital buildings, the share of electricity accounted for 78 per cent and district heating accounted for 8 per cent.
Central heating predominates
A total of 94 per cent of the buildings within the Central government have central heating as their main heating source. In central heating systems, several energy sources can be used. In Norway, the main energy sources used in central heating systems are electricity, heating oils and district heating.
Tables:
Contact
-
Statistics Norway's Information Centre
E-mail: informasjon@ssb.no
tel.: (+47) 21 09 46 42